
It occurred to me that I don’t know much about the trout stocking program in the state. I’ve sort of assumed that most of the trout stocked are rainbow trout, with some browns. The places I’ve fished that are stocked by the state are typically rainbows as far as I know (Big Stoney Creek, Passage Creek, the Jackson River, etc.). I just did a Google search and found a couple references to Virginia stocking both rainbows and brook trout in the Robinson and Rose Rivers near Syria, Virginia (see here too).
Nick Karas, in his seminal work Brook Trout (seminal for those interested in the species, anyway) mentions how programs in Virginia to stock brookies may have impacted the populations I once thought were purely native. He writes, “Virginia’s waters have been stocked with domesticated brook trout for so many years that the integrity of the wild strain has probably been compromised. However, those brook trout populations at the highest elevations are probably little changed genetically from the original [native] stock.” And for better or worse (mostly worse), what’s left for us to catch is almost all in the higher elevations — Shenandoah National Park, the Blue Ridge Parkway, the Alleghenies, etc. In a recent Trout Unlimited interview Mr. Karas again mentions the detrimental effect of stocked brook trout on native populations. It’s been an unfortunately common story throughout the brook trout’s historic range in the east — not just state-run stocking programs but introductions of invasive species by “bucket biologists” are a huge problem in many places, maybe most famously in the Adirondacks. Throw in a little acid rain and other environmental factors and things get bad very quickly for brook trout. In the Adirondacks only 3% of the known brook trout waters remain inhabited by these fish. Three percent.
The Eastern Brook Trout Joint Venture’s website is one place where you can see the gory details on the state of brook trout in the eastern U.S. Trout Unlimited’s Conservation Success Index is another. What is apparent is that stocking streams with invasive fish is just one item on a long list of things conspiring to slowly decimate native trout. From the TU CSI (with my emphasis added): “Like other salmonids in the char genus, brook trout are intolerant of water pollution and non-native fish, and are classic indicators of water quality and ecosystem integrity.” And the CSI’s stark summary of the state of the eastern brook trout:
- 62% of subwatersheds in the historic range are currently occupied (3,282 out of 5,278)
- 1.5% of subwatersheds with brook trout had a Total CSI score > 75 (out of a possible 90)
- Median Range-wide Condition score = 15/25 for extant populations only (range 9-24)
- Median Population Integrity score = 7/15 for extant populations only (range 6-15)
- Median Habitat Integrity score = 13/25 (range 5-24)
- Median Future Security score: 18/24 (range 10-24)
- 8% of subwatersheds priority for protection
- 12% of subwatersheds high priority for reintroduction
- 62% of subwatersheds priority for restoration
Overall, it’s not encouraging. “Non-native fish” are mentioned as threats five times on the CSI’s main page (and “exotic species” is in there at least once, too).
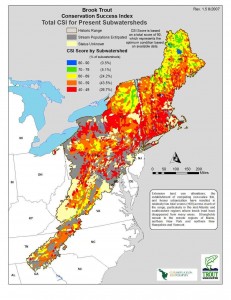
To the left is a map showing the CSI scores for the east coast’s historic brook trout population areas. Anything blue is really good (that’s just 0.5% of the total, all in Maine), green is pretty good (5.1%, and in Virginia we have some of those areas), and the other colors show bigger impacts. Note that gray means extirpated, also known as local extinction, or according to Merriam Webster, “rooted out and destroyed completely” — that may be a good description of people “fishing out” watersheds over the centuries. The main colors that jump out at you when you look at this map are red and orange, the lowest scoring areas, which together comprise 70.2% of the total. These are the areas most affected by “[e]xtensive land use alterations, the establishment of competing non-native fish, and heavy urbanization…”
Anyway, here in Virginia I’m not always sure what to believe now. You hear about native fish in many places, and they are out there. But you can’t be certain that the streams rumored to have native fish have only that, and this is of course because of our long history of stocking domesticated and invasive fish mostly for recreation. Unless you’re a brook trout or a big fan, most would say stocking catchable invasive trout is not all a bad thing. Nevertheless, the impact on native fish is significant.
The Virginia Department of Game and Inland Fisheries is a little vague on the types of fish they raise. The VDGIF hatcheries page does mention one hatchery specifically, Wytheville, that raises brook trout. However, it indicates that “trout from Wytheville are stocked in the waters from roughly Grayson County north to Bland.” All other mentions of trout on that page say only that — “trout” — without differentiating which types of trout are reared, and the stocking schedule doesn’t say anything about what species are stocked, either.

The practice of stocking domesticated brook trout seems less of an issue for the native fish, rightly or wrongly, than the practice of stocking what are really invasive species — rainbows and browns. In Shenandoah National Park I have caught rainbows well inside the park boundary on both the Hughes River and the South Fork of the Thornton River. But officially, it is the brown trout that is the villain. The National Park Service has special brown trout regulations that are kind of goofy (also clarified on the VDGIF website). Any brown trout caught must be disposed of, but there is a seven inch minimum size to harvest brown trout. So if you catch a six incher, you can’t “harvest” it but you have to kill it. OK, but at least the message is clear — do not return them to the stream. Why aren’t there similar regulations for rainbows in the park (i.e. “dispose of them when caught”), since they are also known to compete with and often out-compete brook trout? The NPS website has a page about rainbow trout in the park, and it even notes how they do in fact compete with brook trout. This really begs the question of why the NPS does not treat browns and rainbows the same way, and the bigger question of why Virginia stocks these fish at all in streams inhabited by mostly or totally native strains of brook trout. It’s all especially curious when they tout “National Park Service policy mandates that exotic species will not be allowed to displace native species if displacement can be prevented.” Seems like stocking invasive rainbow trout can surely be prevented.
I should mention here that I am not a biologist, naturalist, fisheries manager, activist or expert on this subject. The folks who do this know more than I do about managing these resources. However, a lot of the concern I read comes from exactly these people. And it just doesn’t make sense that if you want to preserve a native fishery you would stock aggressive invasive species, whatever the type, just downstream.
The NPS website specifically mentions the Rose River, Hughes and Brokenback Run as having browns, and big ones. “Large adult brown trout over 18 inches long with weights in excess of two pounds have been captured within the park in traditional, wild brook trout habitat.” I don’t like the thought of these fish displacing our native species, but catching an 18 inch brown trout on a small stream in the park sounds like a hoot. Then you have to take it home for dinner. I can think of worse things in the name of conservation. There’s that not-all-bad attitude, even with me.
So is it all terrible news? Well, it sort of is. The overall trend is decidedly downward for these fish. There are pockets of effort to reintroduce brook trout populations (see Trout Unlimited’s Shenandoah Headwaters Home Rivers Initiative, for example) but overcoming centuries of damage while human population increases, development continues and climate change is occurring makes it tough to see how things will ever improve for brook trout. We can restore streams and preserve habitat, but what’s gone is probably not coming back and most of the rest is slowly getting ruined. Stocked trout, while providing fun recreation for many of us, is just one factor but may be a lot worse for our native fish than anyone wants to admit.
